SQLAlchemy Session
SQLAlchemy Session Lifecycle Diagram
Below diagram showing the complete SQLAlchemy session lifecycle with all states and transitions:
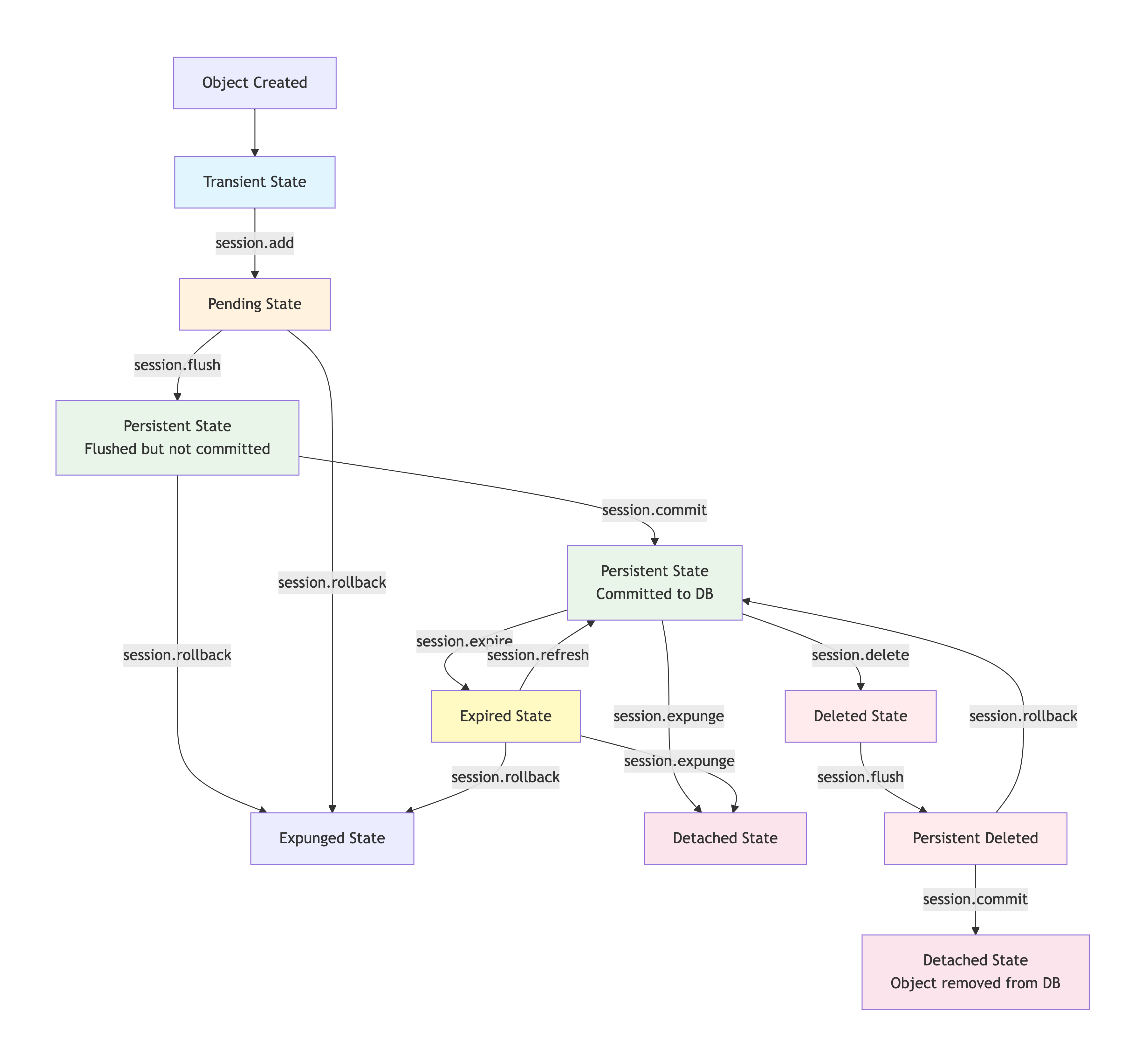
Detailed State Explanations
Section titled “Detailed State Explanations”1. Transient State
Section titled “1. Transient State”# Object exists but is not associated with any sessionuser = User(name="John")# user is in TRANSIENT stateprint(session.is_modified(user)) # False2. Pending State
Section titled “2. Pending State”# Object added to session but not flushedsession.add(user)# user is in PENDING stateprint(user in session) # Trueprint(session.is_modified(user, include_pending=True)) # True3. Persistent State (Flushed)
Section titled “3. Persistent State (Flushed)”# SQL generated but not committedsession.flush()# user is in PERSISTENT state (flushed)print(user.id) # Now has database-generated ID4. Persistent State (Committed)
Section titled “4. Persistent State (Committed)”# Changes persisted to databasesession.commit()# user is in PERSISTENT state (committed)5. Expired State
Section titled “5. Expired State”# After commit, attributes are expiredsession.commit()# user is in EXPIRED stateprint(user.name) # Triggers lazy load from database6. Detached State
Section titled “6. Detached State”# Object no longer associated with sessionsession.expunge(user)# or session.close()# user is in DETACHED stateprint(user in session) # False7. Deleted State
Section titled “7. Deleted State”# Object marked for deletionsession.delete(user)# user is in DELETED statesession.flush() # DELETE statement generatedsession.commit() # Object removed from databaseComplete Lifecycle Example
Section titled “Complete Lifecycle Example”sequenceDiagram
participant O as Object
participant S as Session
participant DB as Database
Note over O,S: 1. TRANSIENT STATE
O->>O: User(name="John")
Note over O,S: 2. PENDING STATE
O->>S: session.add(user)
S->>S: Track changes
Note over O,S: 3. PERSISTENT (Flushed)
S->>S: session.flush()
S->>DB: INSERT INTO users...
DB->>S: Return generated ID
S->>O: Set ID attribute
Note over O,S: 4. PERSISTENT (Committed)
S->>DB: COMMIT
DB->>S: Transaction committed
Note over O,S: 5. EXPIRED STATE
S->>O: Expire attributes
O->>S: Attribute access
S->>DB: SELECT name FROM users...
DB->>S: Return data
S->>O: Refresh attributes
Note over O,S: 6. DETACHED STATE
S->>O: session.expunge()
O->>O: No session association
Note over O,S: 7. DELETED STATE
O->>S: session.delete(user)
S->>S: Mark for deletion
S->>DB: session.flush() - DELETE
DB->>S: Row deleted
S->>DB: session.commit()
O->>O: Object detached
Session State Detection Methods
Section titled “Session State Detection Methods”from sqlalchemy.orm import object_state
def check_object_state(session, obj): """Check the current state of an object relative to a session"""
# Check if object is in session in_session = obj in session
# Get object state state = object_state(obj)
states = { 'transient': state.transient, 'pending': state.pending, 'persistent': state.persistent, 'detached': state.detached, 'deleted': state.deleted, 'modified': session.is_modified(obj), 'expired': state.expired }
return states
# Usage exampledb = SessionLocal()user = User(name="Test")
print("Initial state:", check_object_state(db, user))# transient: True, others: False
db.add(user)print("After add:", check_object_state(db, user))# pending: True
db.flush()print("After flush:", check_object_state(db, user))# persistent: True
db.commit()print("After commit:", check_object_state(db, user))# persistent: True, expired: TrueCommon State Transitions Table
Section titled “Common State Transitions Table”| From State | To State | Trigger | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transient | Pending | session.add() | Object added to session tracking |
| Pending | Persistent | session.flush() | SQL generated, object in database |
| Persistent | Expired | session.commit() | Attributes marked for reload |
| Persistent | Detached | session.expunge() | Object removed from session |
| Persistent | Deleted | session.delete() | Object marked for deletion |
| Expired | Persistent | Attribute access | Lazy reload from database |
| Any | Detached | session.close() | Session closed, all objects detached |
Practical Session Management Patterns
Section titled “Practical Session Management Patterns”Pattern 1: Context Manager with State Tracking
Section titled “Pattern 1: Context Manager with State Tracking”from contextlib import contextmanager
@contextmanagerdef managed_session(session_factory): session = session_factory() try: print("Session started") yield session session.commit() print("Session committed") except Exception as e: session.rollback() print(f"Session rolled back: {e}") raise finally: session.close() print("Session closed")
# Usagewith managed_session(SessionLocal) as session: user = User(name="Managed User") session.add(user) # Automatic commit on success, rollback on exceptionPattern 2: State-aware Operations
Section titled “Pattern 2: State-aware Operations”def safe_save(session, obj): """Safely save an object regardless of its current state""" state = object_state(obj)
if state.detached: # Re-attach detached object session.add(obj) print("Re-attached detached object") elif state.transient: # Add transient object session.add(obj) print("Added transient object") elif state.persistent: # Object already in session print("Object already persistent")
try: session.flush() print("Changes flushed to database") except Exception as e: session.rollback() print(f"Flush failed: {e}") raise
# Usagedb = SessionLocal()user = User(name="Test") # Transientsafe_save(db, user)
user2 = db.query(User).first() # Persistentdb.expunge(user2) # Now detachedsafe_save(db, user2) # Will re-attach